Five New Datasets Released: New Zealand; Australia; Solana Beach, CA TLS; and Sonora, Mexico SFM
OpenTopography is pleased to announce the release of five new international datasets covering areas on both sides of the Pacific. Two of the datasets cover portions of the Wellington and Hope Faults in New Zealand, and were collected by NZ Aerial Mapping with funding from GNS Science (NZ), University Joseph Fourier (France), and Agence Nationale de la Recherche (France). A third, collected near the Burdekin River, Australia by Airborne Research Australia, offers point densities much greater than typical airborne lidar due to atypical overlapping flight grids. The fourth and fifth very high resolution datasets are a terrestrial laser scan (TLS) of the bluff along the City of Solana Beach’s (California, USA) shore by KDM Meridian, and a UAS structure from motion (SfM) photogrammetry dataset of Tecolote Volcano, Sonora, Mexico by a team from Arizona State University and Oklahoma State University.
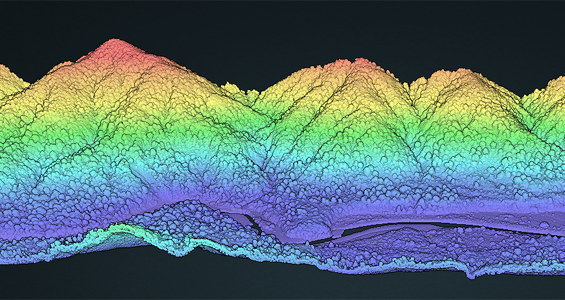
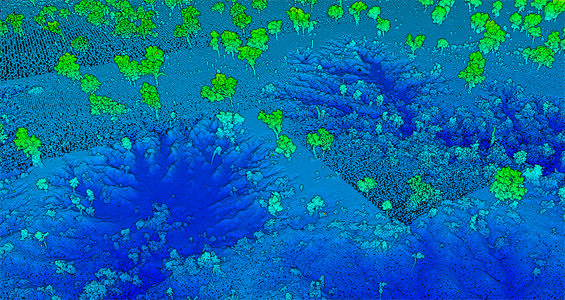
Point cloud visualization images of Wellington Fault, NZ 2010, left, and Very High Resolution Airborne Lidar at Strathalbyn in Queensland, Australia, right, colored by elevation, made with OT’s browser-based 3D visualization tool.

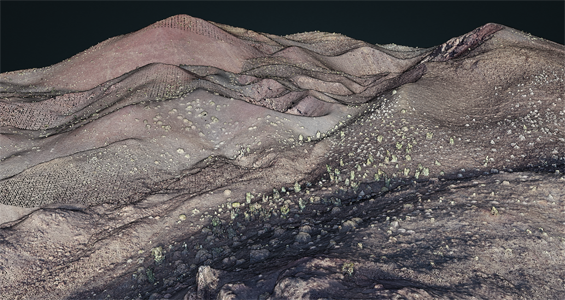
Images made with OT’s browser-based 3D visualization tool using the RGB display attribute of 2016 Solana Beach, CA Bluff Characterization Survey collected by Terrestrial Laser Scan, left, and Photogrammetric Model of the Tecolote Volcano, Sonora, Mexico collected by Structure from Motion through Photogrammetry, right, illustrate the detail of extremely high point densities available through such methods.
